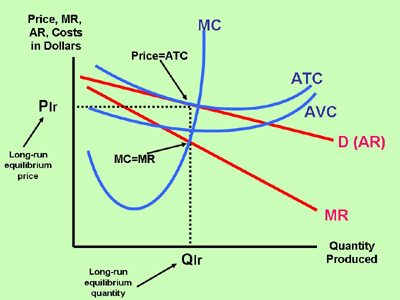
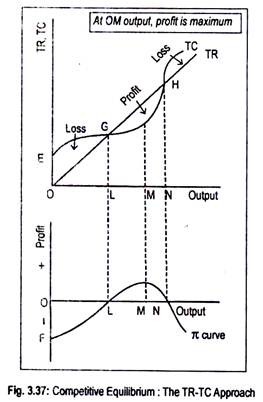
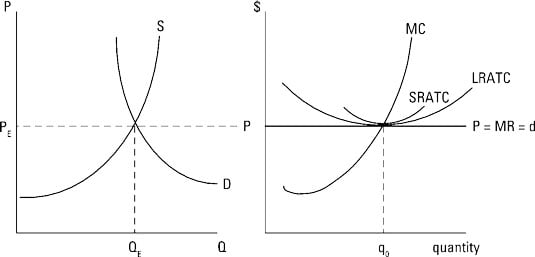
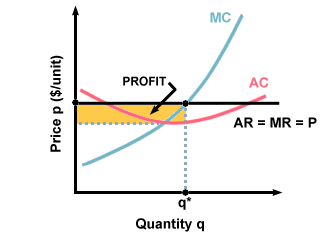
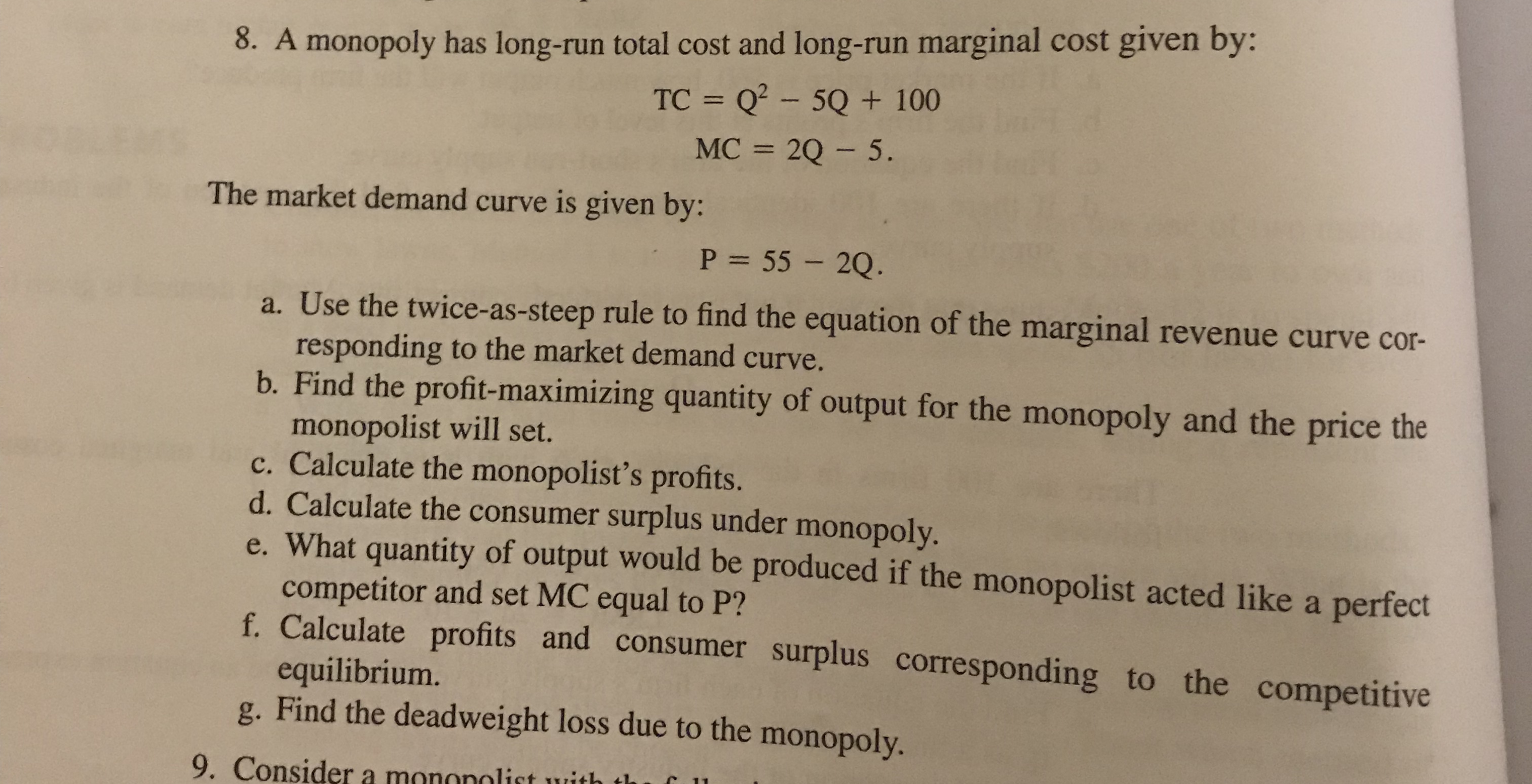Section 2: Short-Run and Long-Run Profit Maximization for a Firm in Monopolistic Competition | Inflate Your Mind

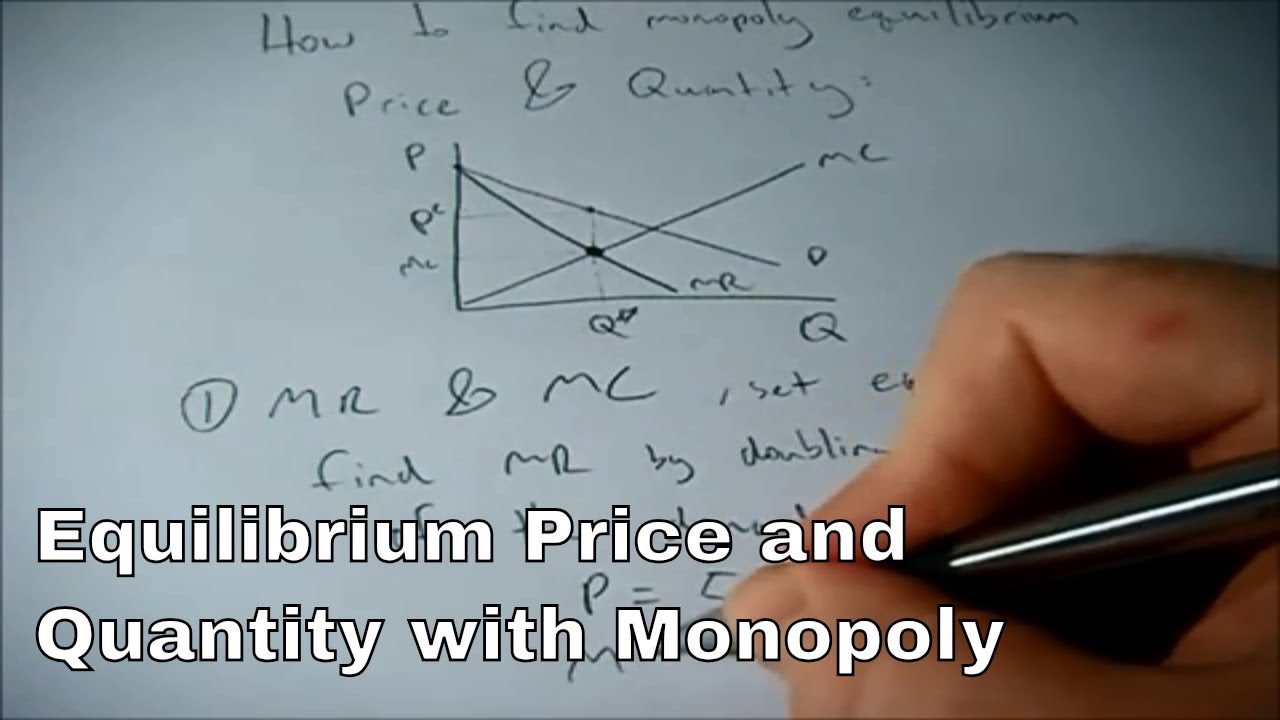
profit maximizing level of price and output from demand functions of two goods . finding revenue - YouTube
![SOLVED: Question [12 marks] A monopolistic produces two goods and y for which the demand functions are P = 138 1.5Q1 Pz = 202 3.5Q2 and total cost function C 4Q + SOLVED: Question [12 marks] A monopolistic produces two goods and y for which the demand functions are P = 138 1.5Q1 Pz = 202 3.5Q2 and total cost function C 4Q +](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/7c993760cb0e4a6e917df7877963d65d.jpg)
SOLVED: Question [12 marks] A monopolistic produces two goods and y for which the demand functions are P = 138 1.5Q1 Pz = 202 3.5Q2 and total cost function C 4Q +

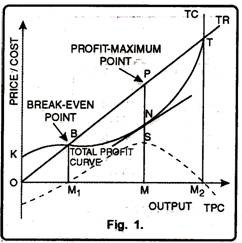
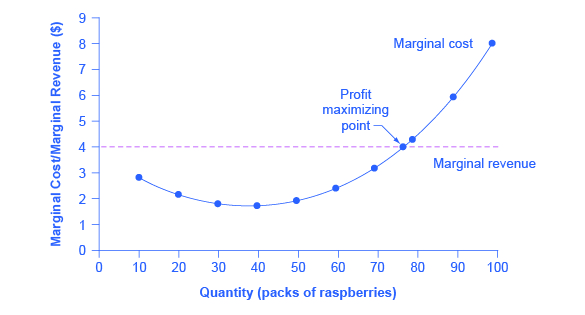
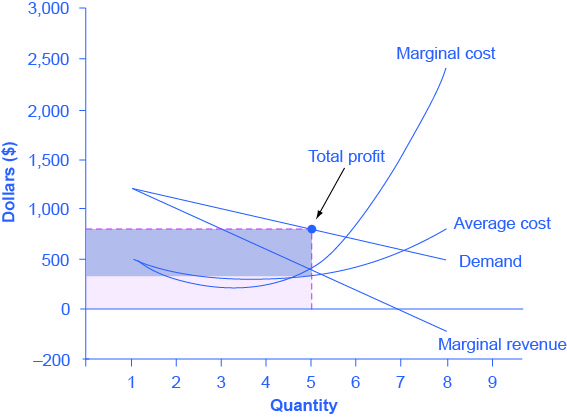
Using the figure, find the profit-maximizing quantity of output when the market equilibrium price of the good is $40. Then calculate the total profit of the firm. | Homework.Study.com

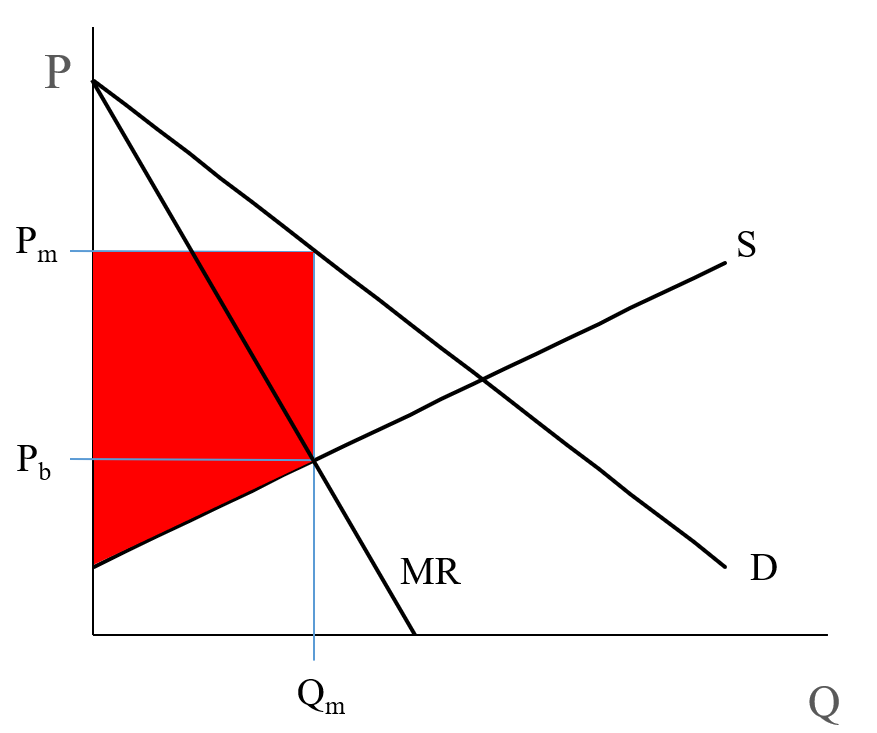
a. What is the monopolist's profit-maximizing output and price? b. Calculate the monopolist's profit/loss, if any. c. What combination of output and price would be produced in this market if it were